Vaccinations, commonly referred to as immunizations, are among the best public health measures available for stopping the spread of infectious diseases. They provide immunity without causing illness by boosting the immune system’s ability to identify and fight off infections. The significance of vaccinations, the different kinds of vaccines, their advantages, and the difficulties posed by vaccination programs are all covered in this article.
Importance of Immunizations
- Disease Prevention: By giving people immunity, vaccinations stop infectious diseases from happening. They have played a significant role in the reduction or eradication of illnesses like measles, polio, and smallpox.
- Herd Immunity: A disease’s overall prevalence is decreased when a sizable section of the populace is immunized. Through herd immunity, this protects people who cannot receive vaccinations, such as those with specific illnesses or allergies.
- Public Health: By averting outbreaks and lessening the strain on healthcare systems, vaccinations improve community health overall. They aid in preventing the expenses and complications that come with treating infectious diseases.
- Global Health: Vaccination programs have global impacts, helping to control and eradicate diseases worldwide. International efforts to distribute vaccines can prevent pandemics and improve health outcomes in underserved regions.
Types of Vaccines
- Live Attenuated Vaccines: These vaccines employ weakened strains of the disease-causing bacteria or virus. They provide enduring immunity and elicit a robust immune response. The vaccines for yellow fever and measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) are two examples.
- Inactivated or Killed Vaccines: Vaccines that use inactivated or killed forms of the pathogen are known as inactivated or killed vaccines. Although they may need booster doses for long-term protection, they are usually safer for people with compromised immune systems. The polio and hepatitis A vaccines are two examples.
- Subunit, Recombinant, or Conjugate Vaccines: Vaccines that are subunit, recombinant, or conjugate only contain particular components of the pathogen, like proteins or sugars. Without the use of live bacteria or viruses, they aid the immune system in identifying and combating the infection. The vaccines against the human papillomavirus (HPV) and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) are two examples.
- mRNA Vaccines: These vaccines direct cells to make a protein that elicits an immune response by using messenger RNA. They have proven to be very effective at warding off illnesses like COVID-19. mRNA vaccines include the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines.
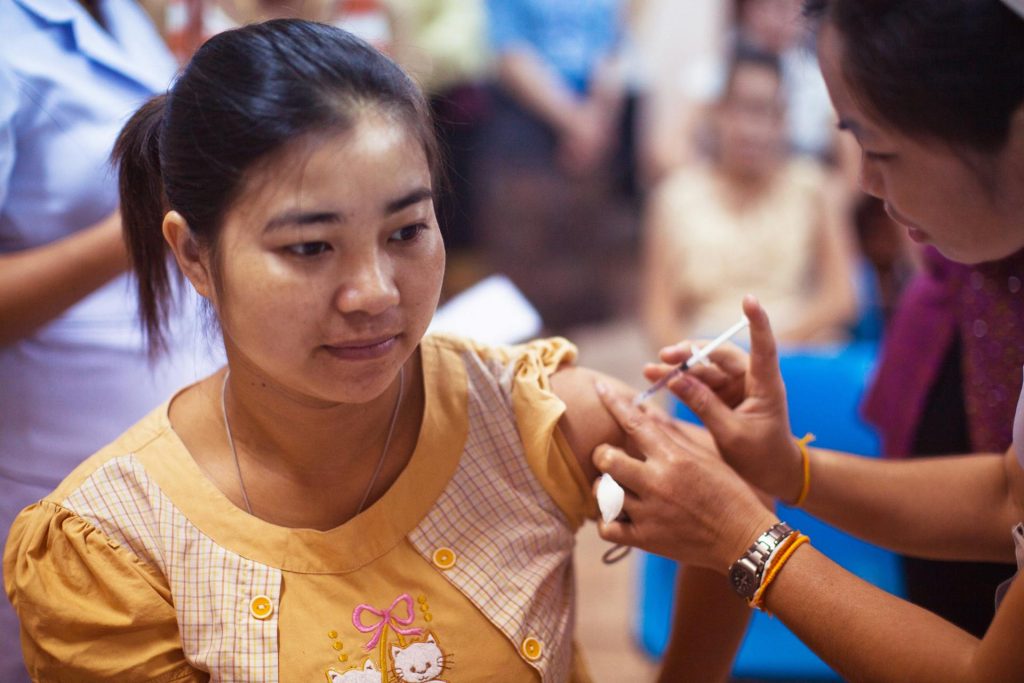

Benefits of Immunizations
- Reduction in Disease Incidence: Vaccines considerably lower the prevalence of a wide range of infectious diseases. For example, polio cases have drastically decreased and smallpox has almost completely disappeared as a result of widespread vaccination.
- Prevention of Complications: Immunizations guard against long-term disability, meningitis, pneumonia, and other complications that can result from illnesses. They shield people from the serious consequences of infections.
- Economic Savings: Vaccinations reduce healthcare costs by preventing disease-related treatments, hospitalizations, and lost productivity. This results in savings for individuals, families, and healthcare systems.
- Improved Quality of Life: Vaccines help to improve general health and quality of life by preventing diseases. They enable people to live healthier lives free from the burden of disease.
Challenges in Immunization Programs
- Vaccine Hesitancy: Due to personal beliefs, false information, or worries about vaccine safety, some people may be reluctant or refuse to get vaccinated. Improving vaccination rates requires addressing vaccine hesitancy through communication and education.
- Access and Distribution: Vaccines may not be widely available in some areas, especially those with limited resources. Successful immunization programs depend on expanding vaccine distribution and guaranteeing fair access.
- Adverse Reactions: Although vaccines are usually safe, they can have unintended consequences. These can range from minor side effects like injection site soreness to uncommon but dangerous adverse events. Sustaining public confidence requires careful monitoring and management of vaccine safety.
- Outbreaks and Emerging Diseases: New infectious diseases and outbreaks can pose challenges for vaccination efforts. Rapid development and deployment of vaccines are necessary to respond to emerging threats, as seen with the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Cost and Funding: The cost of vaccines and the funding required for vaccination programs can be significant. Public and private funding, as well as partnerships with organizations, are necessary to support and sustain immunization efforts.
Conclusion
Immunizations are essential to public health because they protect people from infectious diseases and improve people’s and communities’ general health. Effective immunization practices can be supported and promoted by having a thorough understanding of the various vaccine types, their advantages, and the difficulties encountered in vaccination programs. The benefits of vaccinations will be realized globally, protecting health and preventing disease, provided that ongoing efforts are made to increase vaccine access, address hesitancy, and address emerging diseases.